Chapter #16: How to Create a VDO Volume On a Storage Device
In this chapter, you will learn how to create a VDO volume on a storage device on the RHEL system using deduplication and compression.
VDO, short for Virtual Data Optimizer, is a block virtualization technology that provides inline deduplication and compression of data at a block device level.
The idea of deduplication is quite simple: to remove copies of duplicate data and only retain one copy. When an identical file is added to a block device, it is marked as a duplicate, and the original file is referenced instead. In so doing, VDO helps in saving the block volume’s space.
In this chapter, you will learn how to create a VDO volume on a storage device on the RHEL system.
Install the VDO Volume
To get started, log in to your server and update your RHEL using the dnf command.
sudo dnf update -y
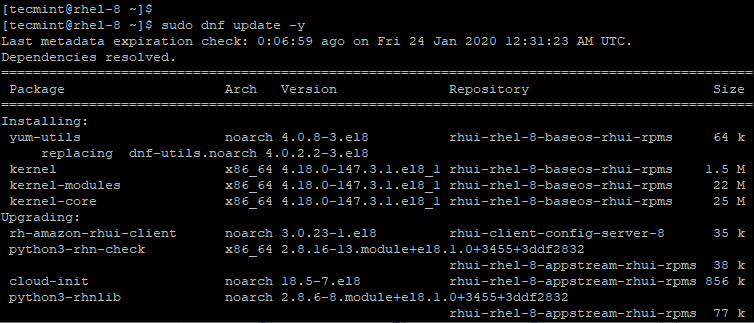
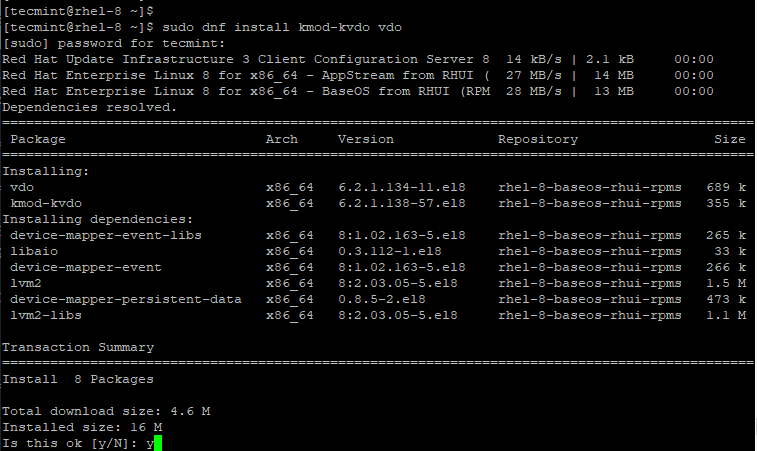
After the update of the packages & kernel is complete, proceed and install the VDO kernel modules and dependencies using the command.
sudo dnf install kmod-kvdo vdo
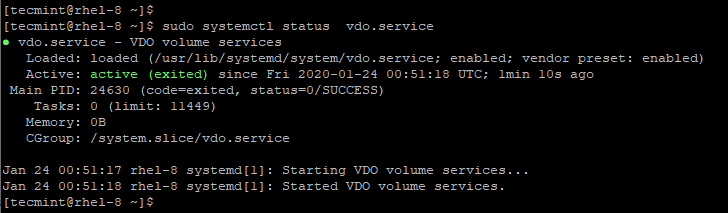
After successful installation, start, enable, and verify the vdo daemon.
sudo systemctl start vdo
sudo systemctl enable vdo
sudo systemctl status vdo
Create a VDO Volume
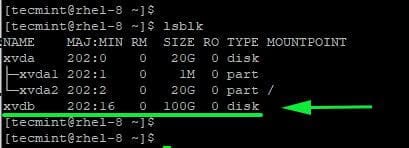
Before creating a vdo volume, ensure that you have an additional hard drive on your system. In this chapter, we have attached an additional volume xvdb. This can be demonstrated by running the lsblk command below.
lsblk
From the output, you can clearly see that the second disk has a capacity of 100GB.
Now, we shall create an empty VDO volume on /dev/xvdb disk.
sudo vdo create --name=vdo1 --device=/dev/xvdb --vdoLogicalSize=300G
You will encounter the error shown.
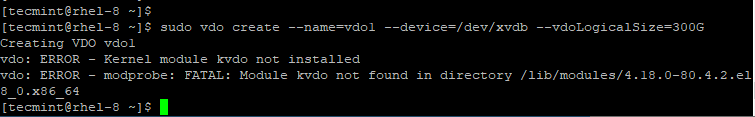
This is a common bug, and the workaround is to simply reboot your server.
reboot
On the second trial, the command will be executed, creating an empty VDO volume on the device /dev/xvdb.
sudo vdo create --name=vdo1 --device=/dev/xvdb --vdoLogicalSize=300G
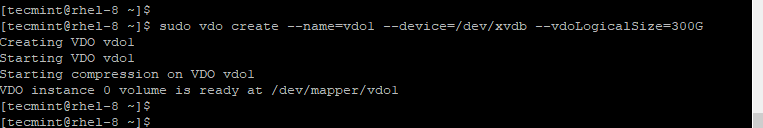
Let’s break down the command and have a look at the option used:
create- This initiates the creation of the VDO volume.--name=vdo1- This gives the volume a label known asvdo1. Feel free to assign any name of your choice.--device=/dev/xvdb- The device option specifies the disk on which the volume will be created.--vdoLogicalSize=300G- This indicates the effective volume capacity to be used by the operating system, in this case, 300G.