pwd Command in Linux
In this article, you’ll learn how to use the pwd command in Linux to print your current working directory with real examples, scripts, and options like -L and -P.

pwd Command in Linuxpwd stands for Print Working Directory. As the name suggests, the pwd command prints the current working directory, i.e., the directory the user is in at that moment.
It returns the current directory with the full absolute path, starting from the root (/). This command is a built-in shell command and is available in most popular shells - bash, Bourne shell, ksh, zsh, etc.
Basic Syntax of pwd
# pwd [OPTION]
Options used with pwd
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -L (logical) | Use PWD from the environment, even if it contains symbolic links |
| -P (physical) | Avoid all symbolic links |
| --help | Display this help and exit |
| --version | Output version information and exit |
-L and -P options are used, -L is given priority. If no option is specified, pwd defaults to -P, avoiding symlinks.The exit status of the command pwd:
| Exit Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Success |
| Non-zero | Failure |
Let’s now discuss some examples of the pwd command to understand its usage!
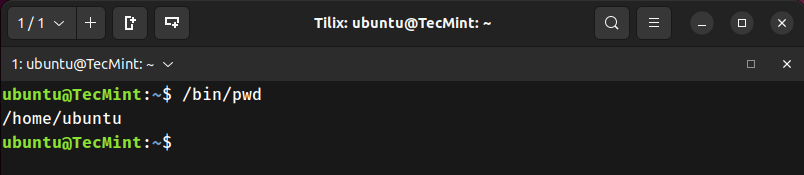
1. Print Your Current Working Directory
Displays the absolute path of the directory you're currently in.
/bin/pwd
2. Create a Symbolic Link and Navigate into It
Create a symbolic link of a folder (say /var/www/html into your home directory as htm). Move to the newly created directory and print the working directory with symbolic links and without symbolic links.
ln -s /var/www/html/ htm
cd htm

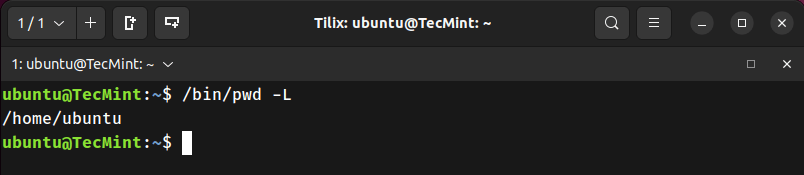
3. Use pwd with -L to Show Logical Path
Prints the current path as stored in the PWD environment variable, including any symlinks.
ubuntu@TecMint:~$ /bin/pwd -L
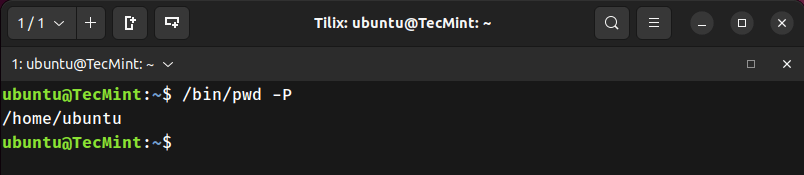
4. Use pwd with -P to Show Physical Path
Resolves and prints the actual physical path, ignoring symlinks.
ubuntu@TecMint:~$ /bin/pwd -P
5. Compare pwd with pwd -P
Check if the output of the command pwd and pwd -P are the same or not i.e., if no options are given at run-time, does pwd take option -P into account or not, automatically?
ubuntu@TecMint:~$ /bin/pwd
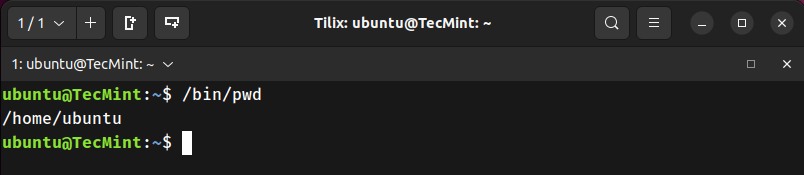
pwd”, it automatically takes option -P into account.6. Display pwd Version
Shows the version and license details of the /bin/pwd binary.
/bin/pwd --version
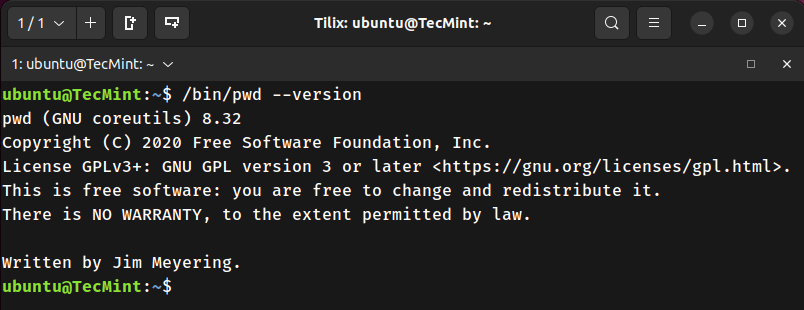
pwd command is often used without options and is rarely, if ever, used with arguments. You might have noticed that in the examples above, the command is executed as /bin/pwd instead of just pwd.So, what’s the difference? When you use pwd by itself, you're typically invoking the shell's built-in version of the command. Different shells may have slightly different implementations of this built-in.
On the other hand, using /bin/pwd explicitly calls the binary version of the command found in the filesystem. Both versions serve the same basic purpose, printing the current working directory, but the binary version generally supports more options and behaves more consistently across different environments.
For more details, refer to your shell’s manual.
7. Difference Between /bin/pwd and Shell Built-in pwd
Identifies all locations where pwd is available, and distinguishes between built-in and binary versions.
type -a pwd
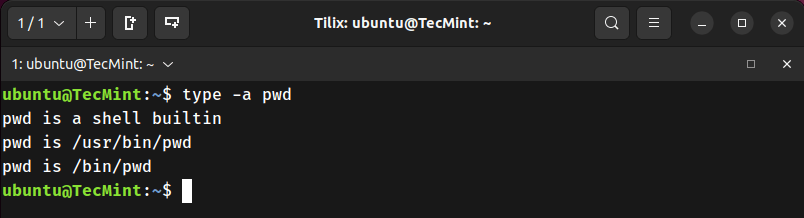
pwd alone uses the shell’s built-in version. /bin/pwd calls the external binary, which often has more options.