mv Command in Linux
Learn how to use the mv command in Linux to move and rename files or directories from one location to another with ease.

The mv command is one of the essential file management utilities in Linux. It is primarily used to move and rename files and directories from one location to another.
Whether you’re organizing your files, archiving old data, or simply renaming items for clarity, mv offers a flexible and efficient way to handle these tasks.
Unlike GUI-based file operations that rely on drag-and-drop, the command-line approach using mv provides greater control, speed, and the ability to perform bulk operations easily with scripting and automation.
Definitely, we can perform this operation using the Graphical User Interface (GUI). However, most Linux users prefer to use the mv command due to its rich functionality and suitability for automation and scripting in professional environments.
mv Command Syntax
The syntax of the mvcommand is similar to other Linux commands. At a high level, it is divided into two parts –options and arguments:
mv [OPTIONS] <SOURCE> <DEST>
mv [OPTIONS] <SOURCE-1> <SOURCE-2> ... <DIRECTORY>
In the above syntax, the square brackets [] represent the optional arguments whereas angular brackets <> represent the mandatory arguments.
Let’s now discuss some basic day-to-day examples of mv commands. So let’s get started.
1. How to Rename a File in Linux
The very basic use of the mv command is to rename a file. So let’s see how to rename a file from the current directory.
First, create a sample file using the touch command:
touch file-1.txt
Now, let’s rename the file using the mv command as follows:
mv file-1.txt file-2.txt
Finally, verify that the file has been renamed successfully using the ls command:
ls -1
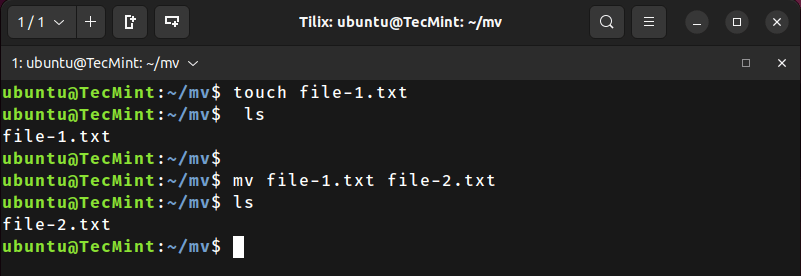
-1 is the number one, which tells ls to list one file per line.2. Enable Verbose Mode in mv Command
Sometimes, we want to know which files or directories are getting renamed. In such cases, we can use the -v option to enable verbose mode.
To understand this, let’s rename the file using verbose mode:
mv -v file-2.txt file-1.txt
renamed 'file-2.txt' -> 'file-1.txt'
In the above output, we can see that the mv command now shows the rename message.
3. How to Rename a Directory in Linux
Similar to files, we can use the mv command to rename a directory. To understand this more clearly, first create a new directory named src:
mkdir src
Now, let’s rename the directory using the following command:
mv -v src dst
renamed 'src' -> 'dst'
4. How to Move Multiple Files to a Directory
Many times, we move files to a single directory for better organization. For example, it is very common practice to keep all audio files in a single directory.
Certainly, we can use the mv command multiple times to achieve this. However, the process quickly becomes time-consuming as the number of files increases. To make it more efficient, we can use the alternative syntax of the mv command.
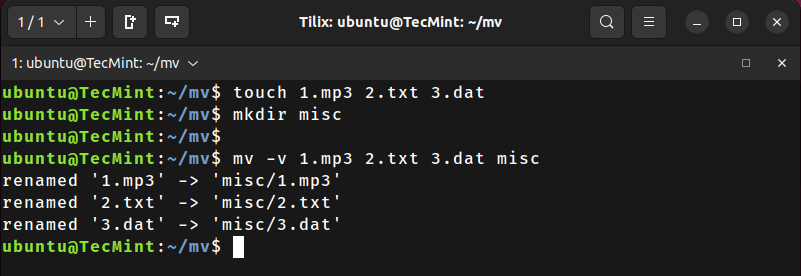
Let’s understand this by creating a few files and a new directory:
touch 1.mp3 2.txt 3.dat
mkdir misc
Now, let’s move all these files to the misc directory using the following command:
mv -v 1.mp3 2.txt 3.dat misc
renamed '1.mp3' -> 'misc/1.mp3'
renamed '2.txt' -> 'misc/2.txt'
renamed '3.dat' -> 'misc/3.dat'
It is important to note that to use this alternative syntax, the destination directory must already exist and must be the last argument of the command.