mkdir Command in Linux
Learn how to use the mkdir command in Linux to create single, multiple, and nested directories with examples, options, and permissions setup.

As Linux users, we use files and directories on a regular basis. Files allow us to store important data whereas directories allow us to organize files in a proper way. In addition to this, we often create a hierarchical directory structure to organize the contents in a better way.
As the name suggests, the mkdir command is used to create a named directory at a given path, which also allows us to create single or multiple directories at once with the required file permissions.
We should note that to use the mkdir command the user must have the required permissions on the parent directory, or else the command will fail with the permission denied error.
Just like other Linux commands, the syntax of the mkdir command is mainly divided into two groups – options and arguments:
mkdir [OPTIONS] ... <DIRECTORY1> <DIRECTORY2> ...
In the above syntax, the square brackets ([]) represent the optional arguments, whereas angular brackets (<>) represent the mandatory arguments.
Basic Usage of mkdir Command in Linux
As the name implies, the mkdir is a short form of the “make directory”. The good thing is that it creates a directory only if a directory or file with the same name doesn’t exist at the given path.
This makes it a very safe command to use, as it won’t overwrite or damage any existing files or directories
Let’s discuss the basic usage of the mkdir command with examples.
1. Create a Directory in Linux
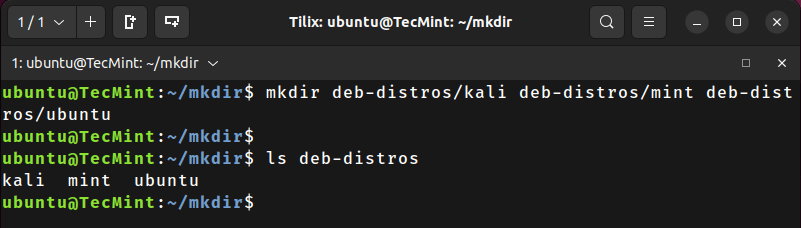
One of the fundamental uses of the mkdir command is to create a named directory at a given path. So let’s create a directory with the name rpm-distros in the current working directory:
mkdir rpm-distros
Now, use the ls command to verify that the directory has been created:
ls
In the first example, we used the relative path with the mkdir command. However, this command also supports the absolute path.
We can use the pwd command or the pwd environment variable to find the absolute path of the current working directory.
So, let’s create the named directory – deb-distros in the current working directory using the absolute path:
mkdir $PWD/deb-distros
Now, verify that the new directory has been created in the current working directory:
ls
2. Create Multiple Directories in Linux
The mkdir command accepts multiple paths as an argument, which allows us to create multiple directories in one go.
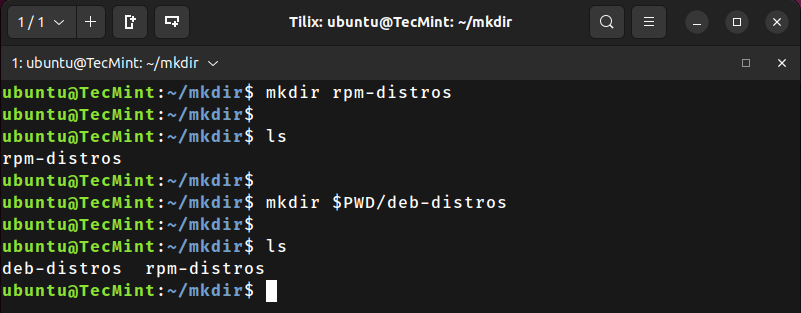
Let’s create three directories inside the deb-distros directory using the single command:
mkdir deb-distros/kali deb-distros/mint deb-distros/ubuntu
Now, let’s list the contents of the deb-distros directory:
ls deb-distros
As we can see, the mkdir command created multiple directories successfully.