cd Command in Linux
In Linux, the `cd` (Change Directory) command is a basic yet essential tool that lets users move between directories, helping them navigate the file system quickly and efficiently.

In Linux, the cd (stands for “Change Directory”) command is one of the most fundamental and frequently used commands. It allows users to navigate the file system by changing their current working directory.
This command enables you to move between directories, access important files, and execute commands in specific locations within the file system.
To understand its usage better, let's explore basic cd commands that use tricks and shortcuts to reduce your efforts on the terminal, saving you valuable time.
1. Changing to a Specific Directory
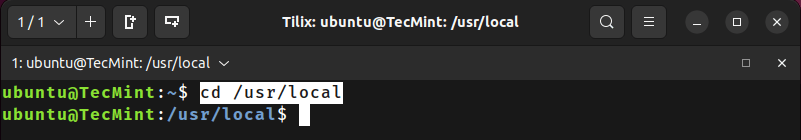
To change from the current directory to the /usr/local, execute this cd command.
cd /usr/local
2. Changing Directory Using Absolute Path
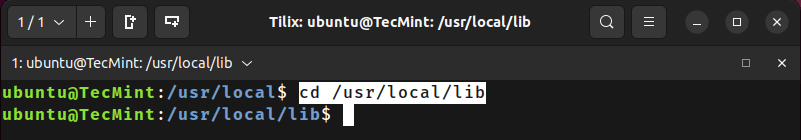
Change from the current directory to the /usr/local/lib using an absolute path.
/usr/local$ cd /usr/local/lib
3. Changing Directory Using Relative Path
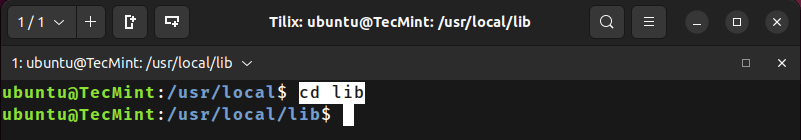
To change from the current working directory to /usr/local/lib using a relative path, execute the stated command:
/usr/local$ cd lib
4. (a) Switching Back to the Previous Directory
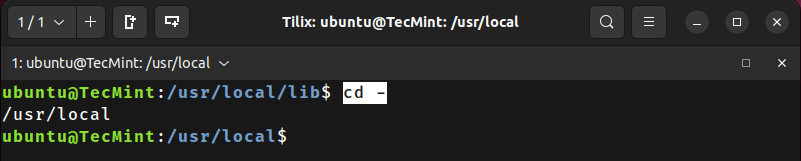
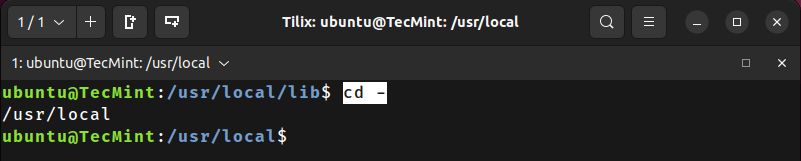
Switch back to the previous directory where you were working earlier, simply by using the - symbol in the “cd” command, as shown:
/usr/local/lib$ cd -
4. (b) Moving to the Parent Directory
To change the current working directory to the parent directory of the current directory, run the cd .. command.
/usr/local/lib$ cd ..
5. Showing the Last Working Directory
To display the last working directory from where we moved (use the -- switch) as shown.
/usr/local$ cd --

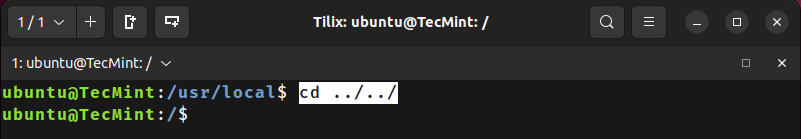
6. Moving Two Directories Up
To move two directories up from where you are now.
/usr/local$ cd ../../
7. Moving to the User's Home Directory
Move to the user's home directory from anywhere by simply using the ~ (tilde symbol) in the cd command:
/usr/local$ cd ~

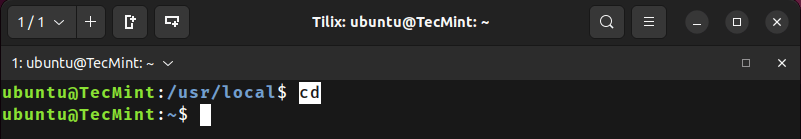
You can even run “cd” without specifying a directory path to take you to your home directory.
/usr/local$ cd
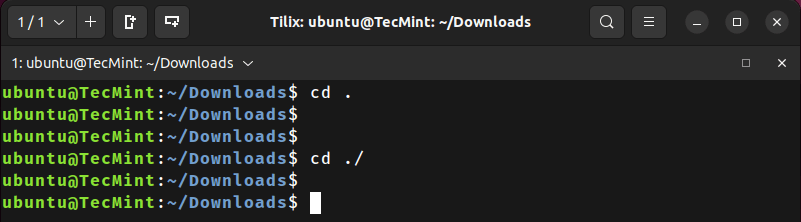
8. Changing to the Current Working Directory
To change the working directory to the current working directory (seems to have no practical use in general).
~/Downloads$ cd .
~/Downloads$ cd ./
9. Changing the Current Working Directory Using an Absolute Path
Let's suppose your present working directory is /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/, change it to /home/ubuntu/Desktop/ in one line command by moving up in the directory hierarchy until /, then using an absolute path.
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages$ cd ../../../../../home/ubuntu/Desktop/
